We use cookies to make your experience better. To comply with the new e-Privacy directive, we need to ask for your consent to set the cookies. Learn more.
Modeling River-Aquifer Interactions with MODFLOW’s SFR2 Package
When modeling complex groundwater systems, few challenges are as nuanced, or as critical, as accurately simulating river-aquifer interactions. When dealing with groundwater flow in areas influenced by surface water, it is essential to understand river-aquifier interactions to create the most accurate simulations. As part of MODFLOW, the Groundwater Modeling System (GMS) offers the SFR2 (StreamFlow Routing) package to model river-aquifer interactions.
What is the SFR2 Package?
SFR2 provides a robust way to simulate gaining and losing streams, flow routing, streambed seepage, and interactions across multiple aquifer layers. SFR2 provides extensive enhancements over RIV and SFR1 packages:
-
Routing of streamflow through a defined steam network.
-
Accounts for interactions between surface water and groundwater.
-
Setting up stream segmentation and routing.
-
Modeling unsaturated flow beneath the streambed.
-
Cumulative stream gains and losses.
-
Connections to multiple MODFLOW layers.
When to Choose SFR2 Over the RIV Package
While both RIV and SFR2 can be used for stream-aquifer exchange modeling, they are optimized for different use cases.
-
Use RIV for simple seepage modeling, large regional-scale models, or streams with constant stages. Quickly build and validate models before using streamflow.
RIV has a much lower computational requirement making it suitable for models where runtime is a major concern but detailed streamflow routing is not required. RIV only tracks flow between river and aquifer, and once water enters the river it is lost to the model.
-
Use SFR2 for projects in riparian zones, wetlands, or basins influenced by stream networks.
SFR2 provides a more detailed understanding of groundwater dynamics in surface-connected systems. SFR2 tracks water so that it can travel downriver and possibly re-enter the aquifer at another point. SFR2 provides output that are essential for water budgeting, permitting, and environmental impact assessments.
Setting Up an SFR2 Model
It is best practice to develop a simple model starting with the RIV package for faster feedback and ease of troubleshooting and then to enable the SFR2 package once the model has been successfully validated.
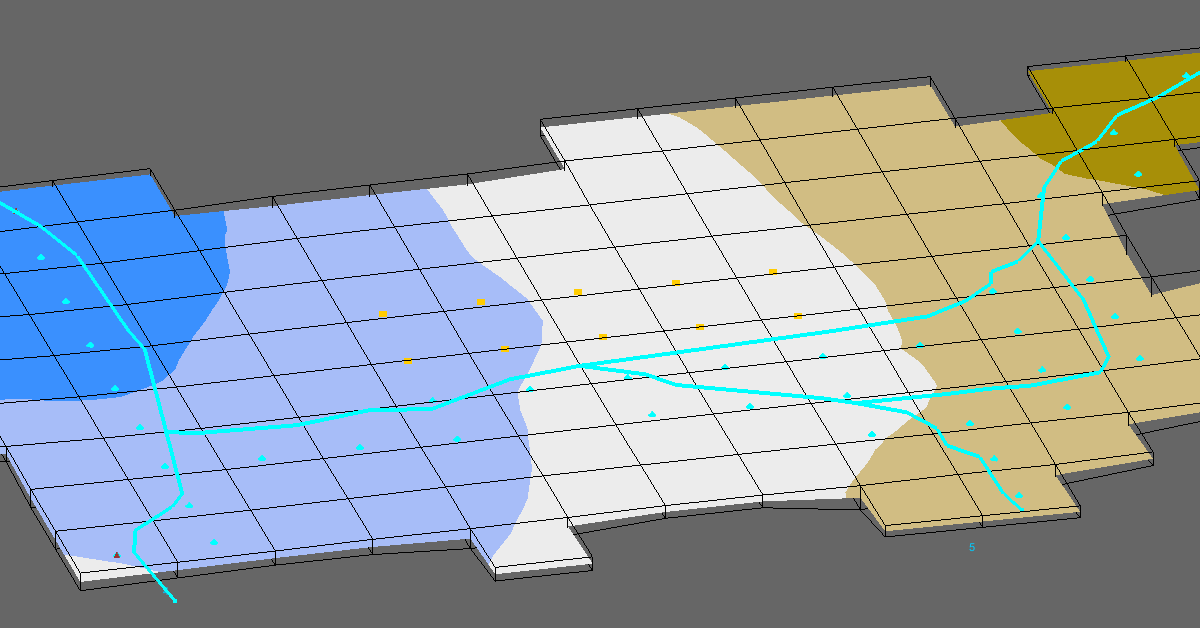
Gather Data Needed by SFR2
The SFR2 package divides streams into arc segments and an associated stream reach with that segment. Before simulation certain data will be needed:
-
Determine inflows and outflows including: Tributaries, diversions, lakes, well locations and schedules, if applicable.
-
Gather field measurements of streambed conductance, thickness, and hydraulic conductivity, or find published values for similar materials.
-
List stream hydrologic or hydraulic changes and attributes such as streambed elevation, width, slope, roughness (Manning’s n), substrate, and conductance.
-
Digitization of stream reach using GIS layers or DEM data.
Building the GMS Conceptual Model
Once the data has been gathered, build the conceptual model in GMS. Building the initial model with the RIV package is recommended. SFR2 requires streambed conductance, thickness, and hydraulic conductivity to simulate seepage controlling how water moves between the stream and aquifer.
-
Create the conceptual model and a coverage for the streams.
-
Create the stream arcs in the Map module.
-
Deconstruct each stream into arc segments based on hydrologic or hydraulic changes, for example, changes in slope or substrate.
-
Create arcs for the stream path. Confirm that the arc direction is correct, and that segments and reaches are numbered sequentially from inflow to outflow.
-
Assign arc attributes to each stream arc such as: streambed elevation, width, slope, roughness (Manning’s n), and conductance.
-
Assign stream segments to the appropriate MODFLOW layer to simulate vertical exchange accurately.
Including the SFR2 Package
In GMS, under MODFLOW Packages, SFR2 needs to be enabled. Then GMS will be able to associate the stream network with steam segments and reaches.
-
Enable SFR2.
-
Configure the routing options, inflow sources, and time-varying flow, if needed.
-
Map the conceptual model to MODFLOW
-
Run the model.
Conclusion
Choose the SFR2 package when more detail is needed about the interaction between a river and aquifer. SFR2 allows you to model the details of stream hydraulics, flow routing and dynamic interaction between an aquifer and the gain or loss from even intermittent streams.
Make use of the SFR2 package and more of MODFLOW by getting GMS today!


