We use cookies to make your experience better. To comply with the new e-Privacy directive, we need to ask for your consent to set the cookies. Learn more.
Understanding the MODFLOW Translator
When importing a MODFLOW file into Groundwater Modeling System (GMS), you may need to translate the file to ensure compatibility with GMS's features and tools. This blog post includes details about the versions of MODFLOW supported by GMS, how GMS uses the translator dialog to transform the MODFLOW file into a version that GMS is able to read and alter, and methods you can use to determine the file version.
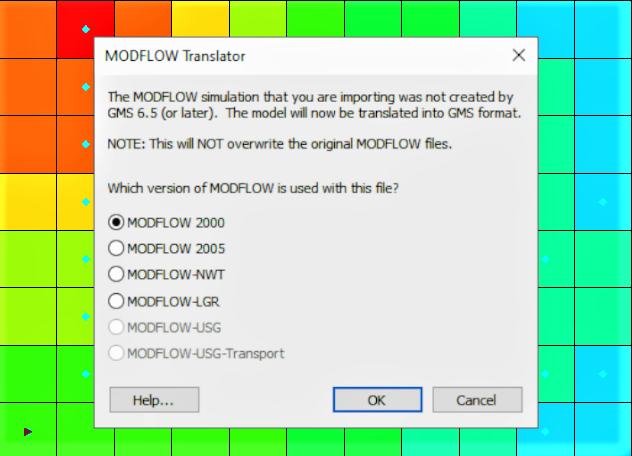
GMS supports MODFLOW versions 88, 96, 2000, 2005, MODFLOW-NWT, MODFLOW LGR, and MODFLOW USG. However, MODFLOW 88 and 96 are only supported as imports and require conversion to MODFLOW 2000. When importing a MODFLOW file into GMS, if the file was not created in GMS 6.5 or later, translation is necessary for full compatibility with GMS's features and tools, so the MODFLOW Translator dialog will appear. GMS will create a copy of the file before performing the translation which will ensure that the original file is preserved, however you should still always double check that all the data was converted successfully and hasn’t been changed and that none of the data has been lost. During the translation process, you can select the appropriate MODFLOW version from the list provided by the translator for accurate interpretation and conversion.
You can also alter the MODFLOW version inside GMS between supported versions by going to Global Options under the MODFLOW menu. It should be noted, however, that while most versions can be changed back and forth, it can’t be changed back from MODFLOW USG Transport.
There are specific indicators for each version of MODFLOW that can help you to determine what kind of MODFLOW file you are working with if you are unsure which file type it is, which you can view by opening the file as a text file. In a MODFLOW 88 file, the third line of the basic package file contains an IUNIT array with 12 or 24 slots, 24 being the more common option. A MODFLOW 96 file, on the other hand, lacks the IUNIT array and instead features the keyword "FREE" on the third line, indicating that data is in free format, or the third line is entirely blank. Files with a *.dis extension are likely to be MODFLOW 2000, 2005, or NWT models, all of which are supported by GMS.
Certain features and versions of MODFLOW are not supported in GMS. If you have more questions about what MODFLOW features are not supported by GMS, you can follow this link to Aquaveo’s wiki for more information. Head over to GMS and see how this can work for your own MODFLOW models today!


