We use cookies to make your experience better. To comply with the new e-Privacy directive, we need to ask for your consent to set the cookies. Learn more.
Fremont River Realignment Study
Utah Department of Transportation

Overview
- 2D finite element model development
- Determine impact of guidebank on flow and velocity
- Evaluate hydraulic impact of bridge piers
Applied Software
- SMS (FESWMS)
Problem
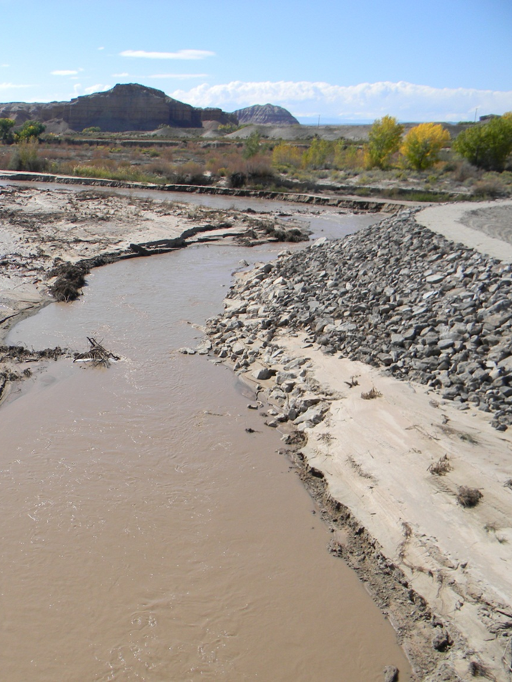
 A large meander bend to the west of the SR-24 bridge crossing of the Fremont River developed on the upstream side of the bridge. The bend caused erosion of the roadway embankment sufficient to require additional protection along the embankment and concern for damage to the roadway and bridge during future flood events. The proposed configuration included a guide bank adjacent to the west bridge abutment on the upstream side, and a realignment of the channel through the point bar directing flow straight through the bridge opening.
A large meander bend to the west of the SR-24 bridge crossing of the Fremont River developed on the upstream side of the bridge. The bend caused erosion of the roadway embankment sufficient to require additional protection along the embankment and concern for damage to the roadway and bridge during future flood events. The proposed configuration included a guide bank adjacent to the west bridge abutment on the upstream side, and a realignment of the channel through the point bar directing flow straight through the bridge opening.
Solution
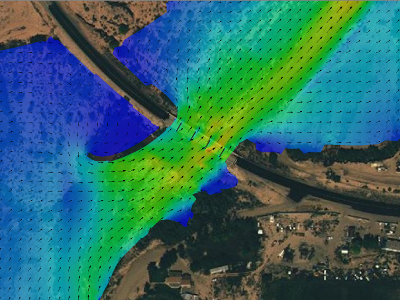 In order to explore the complex flow patterns related to the hydraulics of this bridge crossing, it was determined that a 2-dimensional model would be developed in addition to a 1-dimensional HEC-RAS model. The FHWA FESWMS model was selected as it is the preferred model by FHWA for highway related projects, and would work well with the constraints and data available for this site. The goals of the project were to determine the improvement to the flow conditions from the erosion mitigation measures, and to determine velocity and flow distributions in support of scour analysis at the bridge crossing.
In order to explore the complex flow patterns related to the hydraulics of this bridge crossing, it was determined that a 2-dimensional model would be developed in addition to a 1-dimensional HEC-RAS model. The FHWA FESWMS model was selected as it is the preferred model by FHWA for highway related projects, and would work well with the constraints and data available for this site. The goals of the project were to determine the improvement to the flow conditions from the erosion mitigation measures, and to determine velocity and flow distributions in support of scour analysis at the bridge crossing.
Benefits
As the proposed guidebank dimensions deviated from standard design manuals based on the unique characteristics of the site, a two-dimensional model was key to understanding the feasibility of the proposed design. The guidebank was installed in 2008 and 2009 and provided a long-term solution to the erosion problems at the bridge.