Basin Average Depth
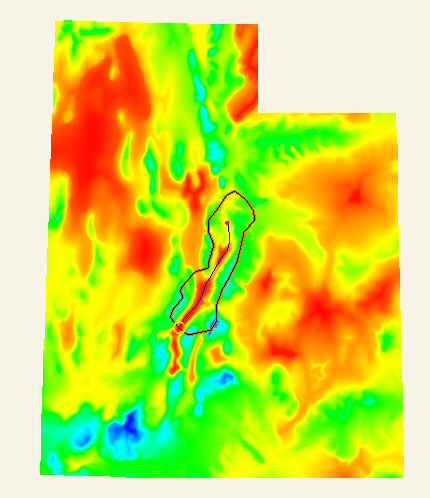
The most common way to develop rainfall estimates for a watershed in a hydrologic simulation is to simply take an average from nearby gages, or from a continuous map (which has been derived from gages). For example in the figure below four different gages are within the watershed, or close enough that measured values are thought to be reflective of what might occur in the watershed. The basin average method is simple. A rainfall depth is determined by taking the numerical average of the gages as follows
This method of computing an average works well where gage data are available. Many agencies, including NOAA, have developed maps like the one below from gages using their best information with respect to topography and meteorological behavior that show rainfall depths for different return periods. Some models, including the MODClark method in HMS and other distributed models, can take advantage of spatially varying rainfall, but for many models an average value is calculated over the watershed or its sub-basins.